commit
8e4fc4b52b
40
README.md
40
README.md
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||||
# 3D Machine Learning
|
3D Machine Learning
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In recent years, tremendous amount of progress is being made in the field of 3D Machine Learning, which is an interdisciplinary field that fuses computer vision, computer graphics and machine learning. This repo is derived from my study notes and will be used as a place for triaging new research papers.
|
In recent years, tremendous amount of progress is being made in the field of 3D Machine Learning, which is an interdisciplinary field that fuses computer vision, computer graphics and machine learning. This repo is derived from my study notes and will be used as a place for triaging new research papers.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
I'll use the following icons to differentiate 3D representations:
|
I'll use the following icons to differentiate 3D representations:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -78,6 +79,7 @@ To see a survey of RGBD datasets, check out Michael Firman's [collection](http:/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>PASCAL3D+ (2014)</b> [[Link]](http://cvgl.stanford.edu/projects/pascal3d.html)
|
<b>PASCAL3D+ (2014)</b> [[Link]](http://cvgl.stanford.edu/projects/pascal3d.html)
|
||||||
<br>12 categories, on average 3k+ objects per category, for 3D object detection and pose estimation.
|
<br>12 categories, on average 3k+ objects per category, for 3D object detection and pose estimation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="http://cvgl.stanford.edu/projects/pascal3d+/pascal3d.png" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="http://cvgl.stanford.edu/projects/pascal3d+/pascal3d.png" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>ModelNet (2015)</b> [[Link]](http://modelnet.cs.princeton.edu/#)
|
<b>ModelNet (2015)</b> [[Link]](http://modelnet.cs.princeton.edu/#)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -176,6 +178,7 @@ This work introduce ScanObjectNN, a new real-world point cloud object dataset ba
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>AI2-THOR: Photorealistic Interactive Environments for AI Agents</b> [[Link]](http://ai2thor.allenai.org/)
|
<b>AI2-THOR: Photorealistic Interactive Environments for AI Agents</b> [[Link]](http://ai2thor.allenai.org/)
|
||||||
<br>AI2-THOR is a photo-realistic interactable framework for AI agents. There are a total 120 scenes in version 1.0 of the THOR environment covering four different room categories: kitchens, living rooms, bedrooms, and bathrooms. Each room has a number of actionable objects.
|
<br>AI2-THOR is a photo-realistic interactable framework for AI agents. There are a total 120 scenes in version 1.0 of the THOR environment covering four different room categories: kitchens, living rooms, bedrooms, and bathrooms. Each room has a number of actionable objects.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://github.com/timzhang642/3D-Machine-Learning/blob/master/imgs/AI2-Thor.jpeg" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://github.com/timzhang642/3D-Machine-Learning/blob/master/imgs/AI2-Thor.jpeg" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>UnrealCV: Virtual Worlds for Computer Vision (2017)</b> [[Link]](http://unrealcv.org/)[[Paper]](http://www.idm.pku.edu.cn/staff/wangyizhou/papers/ACMMM2017_UnrealCV.pdf)
|
<b>UnrealCV: Virtual Worlds for Computer Vision (2017)</b> [[Link]](http://unrealcv.org/)[[Paper]](http://www.idm.pku.edu.cn/staff/wangyizhou/papers/ACMMM2017_UnrealCV.pdf)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -362,6 +365,7 @@ This work introduce ScanObjectNN, a new real-world point cloud object dataset ba
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="http://3dvision.princeton.edu/slide/DSS.jpg" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="http://3dvision.princeton.edu/slide/DSS.jpg" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>Three-Dimensional Object Detection and Layout Prediction using Clouds of Oriented Gradients (2016)</b> [[CVPR '16 Paper]](https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/Ren_Three-Dimensional_Object_Detection_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf) [[CVPR '18 Paper]](http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Ren_3D_Object_Detection_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf) [[T-PAMI '19 Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.04725)
|
<b>Three-Dimensional Object Detection and Layout Prediction using Clouds of Oriented Gradients (2016)</b> [[CVPR '16 Paper]](https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/Ren_Three-Dimensional_Object_Detection_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf) [[CVPR '18 Paper]](http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Ren_3D_Object_Detection_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf) [[T-PAMI '19 Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.04725)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://github.com/luvegood/3D-Machine-Learning/blob/master/imgs/Three-Dimensional%20Object%20Detection%20and%20Layout%20Prediction%20using%20Clouds%20of%20Oriented%20Gradients.png" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://github.com/luvegood/3D-Machine-Learning/blob/master/imgs/Three-Dimensional%20Object%20Detection%20and%20Layout%20Prediction%20using%20Clouds%20of%20Oriented%20Gradients.png" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>DeepContext: Context-Encoding Neural Pathways for 3D Holistic Scene Understanding (2016)</b> [[Paper]](http://deepcontext.cs.princeton.edu/)
|
<b>DeepContext: Context-Encoding Neural Pathways for 3D Holistic Scene Understanding (2016)</b> [[Paper]](http://deepcontext.cs.princeton.edu/)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -492,7 +496,7 @@ We introduce a novel convolution operator for point clouds that achieves rotatio
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="3d_synthesis_model_based" />
|
<a name="3d_synthesis_model_based" />
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
_Parametric Morphable Model-based methods_
|
### Parametric Morphable Model-based methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>A Morphable Model For The Synthesis Of 3D Faces (1999)</b> [[Paper]](http://gravis.dmi.unibas.ch/publications/Sigg99/morphmod2.pdf)[[Code]](https://github.com/MichaelMure/3DMM)
|
<b>A Morphable Model For The Synthesis Of 3D Faces (1999)</b> [[Paper]](http://gravis.dmi.unibas.ch/publications/Sigg99/morphmod2.pdf)[[Code]](https://github.com/MichaelMure/3DMM)
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="40%" src="http://mblogthumb3.phinf.naver.net/MjAxNzAzMTdfMjcz/MDAxNDg5NzE3MzU0ODI3.9lQioLxwoGmtoIVXX9sbVOzhezoqgKMKiTovBnbUFN0g.sXN5tG4Kohgk7OJEtPnux-mv7OAoXVxxCyo3SGZMc6Yg.PNG.atelierjpro/031717_0222_DataDrivenS4.png?type=w420" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="40%" src="http://mblogthumb3.phinf.naver.net/MjAxNzAzMTdfMjcz/MDAxNDg5NzE3MzU0ODI3.9lQioLxwoGmtoIVXX9sbVOzhezoqgKMKiTovBnbUFN0g.sXN5tG4Kohgk7OJEtPnux-mv7OAoXVxxCyo3SGZMc6Yg.PNG.atelierjpro/031717_0222_DataDrivenS4.png?type=w420" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
@ -503,9 +507,11 @@ The code demonstrates how to 1) reconstruct textured 3D faces from images, 2) fi
|
||||||
<p align="center"> <img width="50%" src="https://github.com/TimoBolkart/TF_FLAME/blob/master/gifs/model_variations.gif"></p>
|
<p align="center"> <img width="50%" src="https://github.com/TimoBolkart/TF_FLAME/blob/master/gifs/model_variations.gif"></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>The Space of Human Body Shapes: Reconstruction and Parameterization from Range Scans (2003)</b> [[Paper]](http://grail.cs.washington.edu/projects/digital-human/pub/allen03space-submit.pdf)
|
<b>The Space of Human Body Shapes: Reconstruction and Parameterization from Range Scans (2003)</b> [[Paper]](http://grail.cs.washington.edu/projects/digital-human/pub/allen03space-submit.pdf)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://ai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com/figures/2016-11-08/46d39b0e21ae956e4bcb7a789f92be480d45ee12/7-Figure10-1.png" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://ai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com/figures/2016-11-08/46d39b0e21ae956e4bcb7a789f92be480d45ee12/7-Figure10-1.png" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>SMPL-X: Expressive Body Capture: 3D Hands, Face, and Body from a Single Image (2019)</b> [[Paper]](https://ps.is.tuebingen.mpg.de/uploads_file/attachment/attachment/497/SMPL-X.pdf)[[Video]](https://youtu.be/XyXIEmapWkw)[[Code]](https://github.com/vchoutas/smplify-x)
|
<b>SMPL-X: Expressive Body Capture: 3D Hands, Face, and Body from a Single Image (2019)</b> [[Paper]](https://ps.is.tuebingen.mpg.de/uploads_file/attachment/attachment/497/SMPL-X.pdf)[[Video]](https://youtu.be/XyXIEmapWkw)[[Code]](https://github.com/vchoutas/smplify-x)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center"> <img width="50%" src="https://github.com/vchoutas/smplify-x/blob/master/images/teaser_fig.png"></p>
|
<p align="center"> <img width="50%" src="https://github.com/vchoutas/smplify-x/blob/master/images/teaser_fig.png"></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>PIFuHD: Multi-Level Pixel Aligned Implicit Function for High-Resolution 3D Human Digitization (CVPR 2020)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.00452.pdf)[[Video]](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uEDqCxvF5yc&feature=youtu.be)[[Code]](https://github.com/facebookresearch/pifuhd)
|
<b>PIFuHD: Multi-Level Pixel Aligned Implicit Function for High-Resolution 3D Human Digitization (CVPR 2020)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.00452.pdf)[[Video]](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uEDqCxvF5yc&feature=youtu.be)[[Code]](https://github.com/facebookresearch/pifuhd)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -549,9 +555,10 @@ Dense 3D Reconstructions from a Single Image (2017)</b> [[Paper]](http://ci2cv.n
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="3d_synthesis_template_based" />
|
<a name="3d_synthesis_template_based" />
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
_Part-based Template Learning methods_
|
### Part-based Template Learning methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>Modeling by Example (2004)</b> [[Paper]](http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~funk/sig04a.pdf)
|
<b>Modeling by Example (2004)</b> [[Paper]](http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~funk/sig04a.pdf)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="20%" src="http://gfx.cs.princeton.edu/pubs/Funkhouser_2004_MBE/chair.jpg" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="20%" src="http://gfx.cs.princeton.edu/pubs/Funkhouser_2004_MBE/chair.jpg" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<b>Model Composition from Interchangeable Components (2007)</b> [[Paper]](http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring11/cos598A/pdfs/Kraevoy07.pdf)
|
<b>Model Composition from Interchangeable Components (2007)</b> [[Paper]](http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring11/cos598A/pdfs/Kraevoy07.pdf)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -598,7 +605,7 @@ _Part-based Template Learning methods_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="3d_synthesis_dl_based" />
|
<a name="3d_synthesis_dl_based" />
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
_Deep Learning Methods_
|
### Deep Learning Methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
:camera: <b>Learning to Generate Chairs, Tables and Cars with Convolutional Networks (2014)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.5928.pdf)
|
:camera: <b>Learning to Generate Chairs, Tables and Cars with Convolutional Networks (2014)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.5928.pdf)
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://zo7.github.io/img/2016-09-25-generating-faces/chairs-model.png" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://zo7.github.io/img/2016-09-25-generating-faces/chairs-model.png" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
@ -726,7 +733,14 @@ _Deep Learning Methods_
|
||||||
:pill: <b>ComplementMe: Weakly-Supervised Component Suggestions for 3D Modeling (2017)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.01841.pdf)
|
:pill: <b>ComplementMe: Weakly-Supervised Component Suggestions for 3D Modeling (2017)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.01841.pdf)
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://mhsung.github.io/assets/images/complement-me/figure_2.png" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://mhsung.github.io/assets/images/complement-me/figure_2.png" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
:space_invader: <b>Learning Descriptor Networks for 3D Shape Synthesis and Analysis (2018 CVPR)</b> [[Project]](http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~jxie/3DEBM/) [[Paper]](http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~jxie/3DDescriptorNet/3DDescriptorNet_file/doc/3DDescriptorNet.pdf) [[Code](https://github.com/jianwen-xie/3DDescriptorNet)]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
An energy-based 3D shape descriptor network is a deep energy-based model for volumetric shape patterns. The maximum likelihood training of the model follows an “analysis by synthesis” scheme and can be interpreted as a mode seeking and mode shifting process. The model can synthesize 3D shape patterns by sampling from the probability distribution via MCMC such as Langevin dynamics. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed model can generate realistic 3D shape patterns and can be useful for 3D shape analysis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
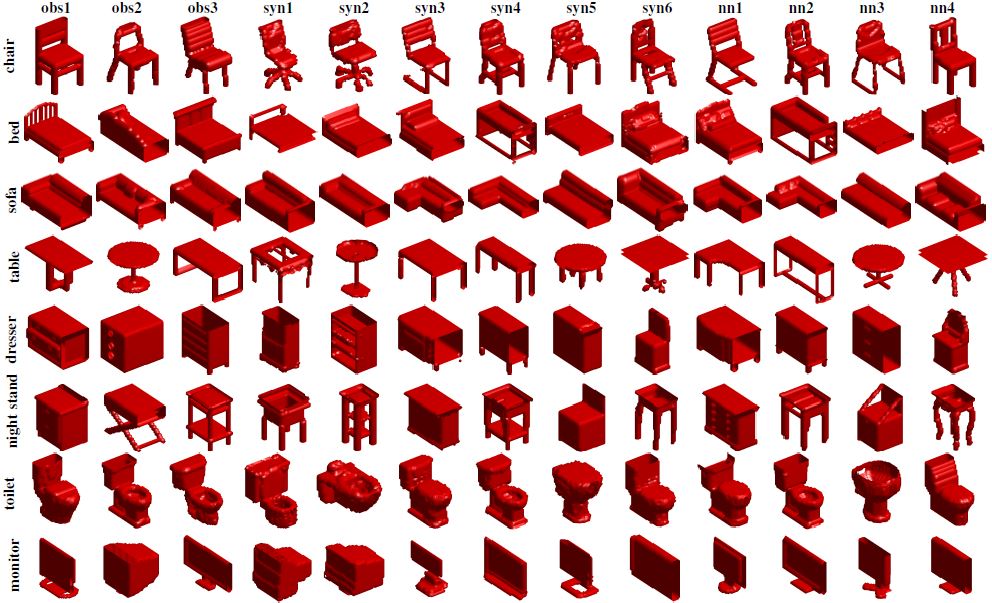
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
:game_die: <b>PU-Net: Point Cloud Upsampling Network (2018)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.06761.pdf) [[Code]](https://github.com/yulequan/PU-Net)
|
:game_die: <b>PU-Net: Point Cloud Upsampling Network (2018)</b> [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.06761.pdf) [[Code]](https://github.com/yulequan/PU-Net)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="http://appsrv.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~lqyu/indexpics/Pu-Net.png" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="http://appsrv.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~lqyu/indexpics/Pu-Net.png" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
:camera::space_invader: <b>Multi-view Consistency as Supervisory Signal for Learning Shape and Pose Prediction (2018 CVPR)</b> [[Paper]](https://shubhtuls.github.io/mvcSnP/)
|
:camera::space_invader: <b>Multi-view Consistency as Supervisory Signal for Learning Shape and Pose Prediction (2018 CVPR)</b> [[Paper]](https://shubhtuls.github.io/mvcSnP/)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -840,6 +854,24 @@ Deformable Shape Completion with Graph Convolutional Autoencoders (2018 CVPR)</b
|
||||||
:gem::game_die: <b>GAMesh: Guided and Augmented Meshing for Deep Point Networks (3DV 2020)</b> [[Project]](https://www.ics.uci.edu/~agarwal/GAMesh/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.09774) [[Code]](https://github.com/nitinagarwal/GAMesh)
|
:gem::game_die: <b>GAMesh: Guided and Augmented Meshing for Deep Point Networks (3DV 2020)</b> [[Project]](https://www.ics.uci.edu/~agarwal/GAMesh/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.09774) [[Code]](https://github.com/nitinagarwal/GAMesh)
|
||||||
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://www.ics.uci.edu/~agarwal/3DV_2020.png" /></p>
|
<p align="center"><img width="50%" src="https://www.ics.uci.edu/~agarwal/3DV_2020.png" /></p>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
:space_invader: <b>Generative VoxelNet: Learning Energy-Based Models for 3D Shape Synthesis and Analysis (2020 TPAMI)</b> [[Paper]](http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~jxie/3DEBM/3DEBM_file/doc/gVoxelNet.pdf)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This paper proposes a deep 3D energy-based model to represent volumetric shapes. The maximum likelihood training of the model follows an “analysis by synthesis” scheme. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed model can generate high-quality 3D shape patterns and can be useful for a wide variety of 3D shape analysis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
:game_die: <b>Generative PointNet: Deep Energy-Based Learning on Unordered Point Sets for 3D Generation, Reconstruction and Classification (2021 CVPR) </b> [[Project]](http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~jxie/GPointNet/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.01301.pdf) [[Code](https://github.com/fei960922/GPointNet)]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Generative PointNet is an energy-based model of unordered point clouds, where the energy function is parameterized by an input-permutation-invariant bottom-up neural network. The model can be trained by MCMC-based maximum likelihood learning, or a short-run MCMC toward the energy-based model as a flow-like generator for point cloud reconstruction and interpolation. The learned point cloud representation can be useful for point cloud classification.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<a name="material_synthesis" />
|
<a name="material_synthesis" />
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Texture/Material Analysis and Synthesis
|
## Texture/Material Analysis and Synthesis
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 167 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 48 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 137 KiB |
Loading…
Reference in New Issue